What is ICM?
The Islamic Capital Market is a market in which capital market transactions, operations, and activities are conducted in accordance with Shari’ah principles. The term ‘Islamic’ in the ‘Islamic capital market’ is to emphasizes and underlines that those transactions in such a market must be free of the inclusion of prohibited activities in Islam, such as usury (riba), gambling (maysir) and ambiguity (gharar). In Malaysia, the Islamic capital markets, such as retail banking, are thriving, where it has been seen that Sukuk has shown a tremendous expansion in the capital markets. Murabaḥah, Muḍarabah, Musharakah, Ijarah, and Tawarruq are some of the terms that are used in Malaysia for Shari’ah-compliant financial products.
The Securities Commission Malaysia (SCM) announced the issuance of Shari’ah criteria and Shari’ah approved securities, in May 1996. Following this announcement, Islamic capital markets received more attention from the investors that are interested in investing in Shari'ah-compliant markets as an alternative to the capital markets. Islamic capital markets in Malaysia are governed under the Securities Commission Malaysia and the Capital Market Services Act (CMSA) 2007. On top of that, Malaysia's Islamic capital market remains an enticing attraction for all the stakeholders up until this day. The SC’s initial objective in establishing an Islamic Capital Market Department (ICMD) was to offer much-needed infrastructure support. The ICMD's mandate is to conduct development and research activities, such as developing and facilitating a long-term plan to enhance the Islamic capital market in Malaysia.
Various ways have been used to establish Islamic financial products and services that are market compatible. One approach is to change the products and services in the conventional system so that they do not contradict the Shari’ah. In contrast, the second approach is to develop a new product or service that is solely based on Shari’ah principles and adheres to various Shari’ah concepts. Shari’ah-compliant goods, for investors, have evolved through multiple stages since 1990, with the launch of numerous large-scale initiatives. Furthermore, the Islamic Capital Market has several projects in the works to meet the demands of investors, shareholders, and businesses who prefer Shari'ah-compliant markets to conventional markets.
With the expansion of the Islamic banking and takaful sectors, the importance of the Islamic capital market has grown. Furthermore, the Islamic financial sector lacks Islamic financial instruments capable of providing more Shariah-compliant products and services. As a result, Islamic capital markets must provide Shari'ah-compliant instruments and meet investor demand. However, although the Islamic capital market has unique qualities such as risk-sharing, property rights, rights, and duties of the individual and society while developing products, it sadly tends to imitate all conventional capital market products, which will harm its image in the long term.
However, non-Muslim investors are now becoming interested in Islamic capital markets. While these products provided an opportunity to diversify portfolios, they were generally straightforward, clear, and at low risk. While the economic crisis has called for more regulations, Islamic financial institutions have been relatively safe because Shari’ah law prohibits speculating, which is thought to be the root cause of the current crisis. As a result, the global crisis has raised awareness of Islamic financing in markets all over the world. Several non-Muslim countries, including the United Kingdom, Germany, Spain, and Italy, are considering the regulatory and legal aspects of Islamic financing products. With the growing popularity of Islamic financing among non-Muslim countries, large Western banks have begun to offer Islamic financial products through a separate Islamic window. HSBC, for example, launched its independent Islamic financial firm, HSBC Amanah, in 1998. In 2004, UBS established a separate bank in Dubai to provide Islamic financing services to Middle Eastern clients.

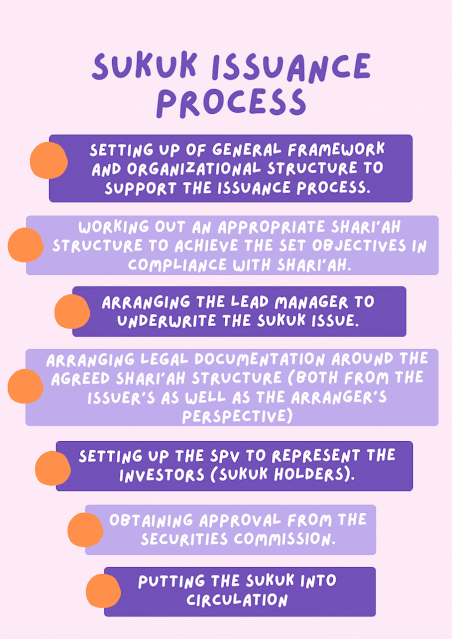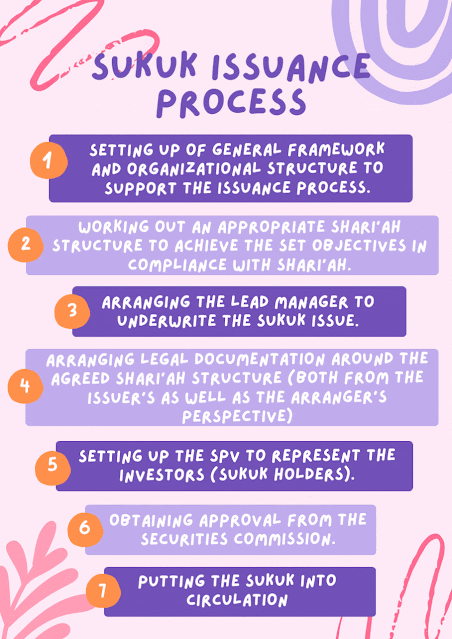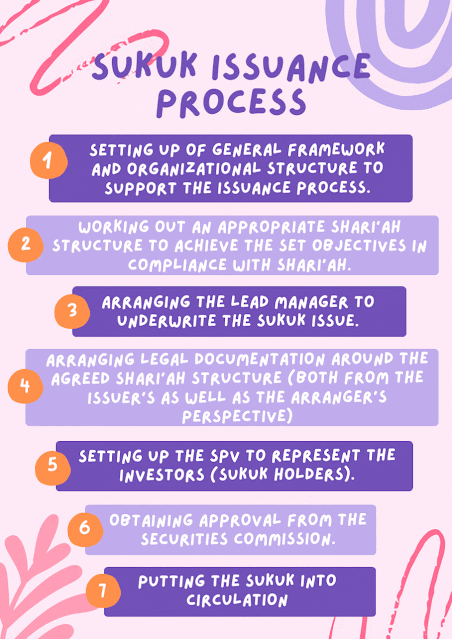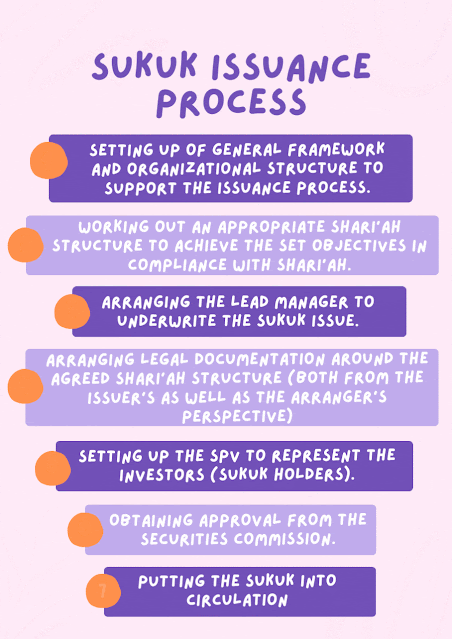
.gif)

Comments
Post a Comment